BlogWhat is DeFi
Credits to @macrovector at freepik.com
Since the DeFi summer of 2020, one of the hottest topics discussed in the and space is decentralized finance or DeFi. With massive growths in total value locked and active users of various protocols, we have seen a sort of crypto Gold Rush accompanied by a Wild West-style code of conduct.
In DeFi, we see the great benefits of decentralization, unheard-of returns on investment, equal access to all users, and much more. But we also see the flip side of this financial freedom like scams, rug-pulls, insider trading, network outages, and hacks. Let's take a closer look into what DeFi is and why it is vital to the future success of cryptocurrencies and digital assets.
What is DeFi?
Decentralized finance is the term to describe the collection of non-custodial decentralized financial services and the various protocols that operate them. The purpose of DeFi is simple, to bring equal access, fully transparent, and non-custodial financial services to anyone globally with an internet connection.
Much like traditional centralized financial services, DeFi has many use cases and helps create or maintain wealth for individuals by putting their assets to work. We will discuss them in greater detail later, but the most popular DeFi services offered are lending/borrowing, exchanges, options trading, derivatives, payments, and yield farming.
Benefits of DeFi
Many problems exist with the conventional custodial financial services offered today that DeFi seeks to solve.
- Unequal access to custodian financial services like bank accounts or lending/borrowing.
- Lack of access to financial services can prevent employment, generational wealth, homeownership, and more.
- Financial custodians can block payments at any time.
- Giving access to your private information to custodians to use as they see fit.
- Governments and centralized institutions can close down whole markets at will (AMC and GME stocks).
- Trading hours are often limited to business hours of a specific time zone.
- Money transfers and payments can take days to settle and often suffer from human error.
- Intermediaries or "middleman" cause custodian financial services to charge premiums just to use their service.
When we compare DeFi against the traditional financial system we can clearly see the benefits
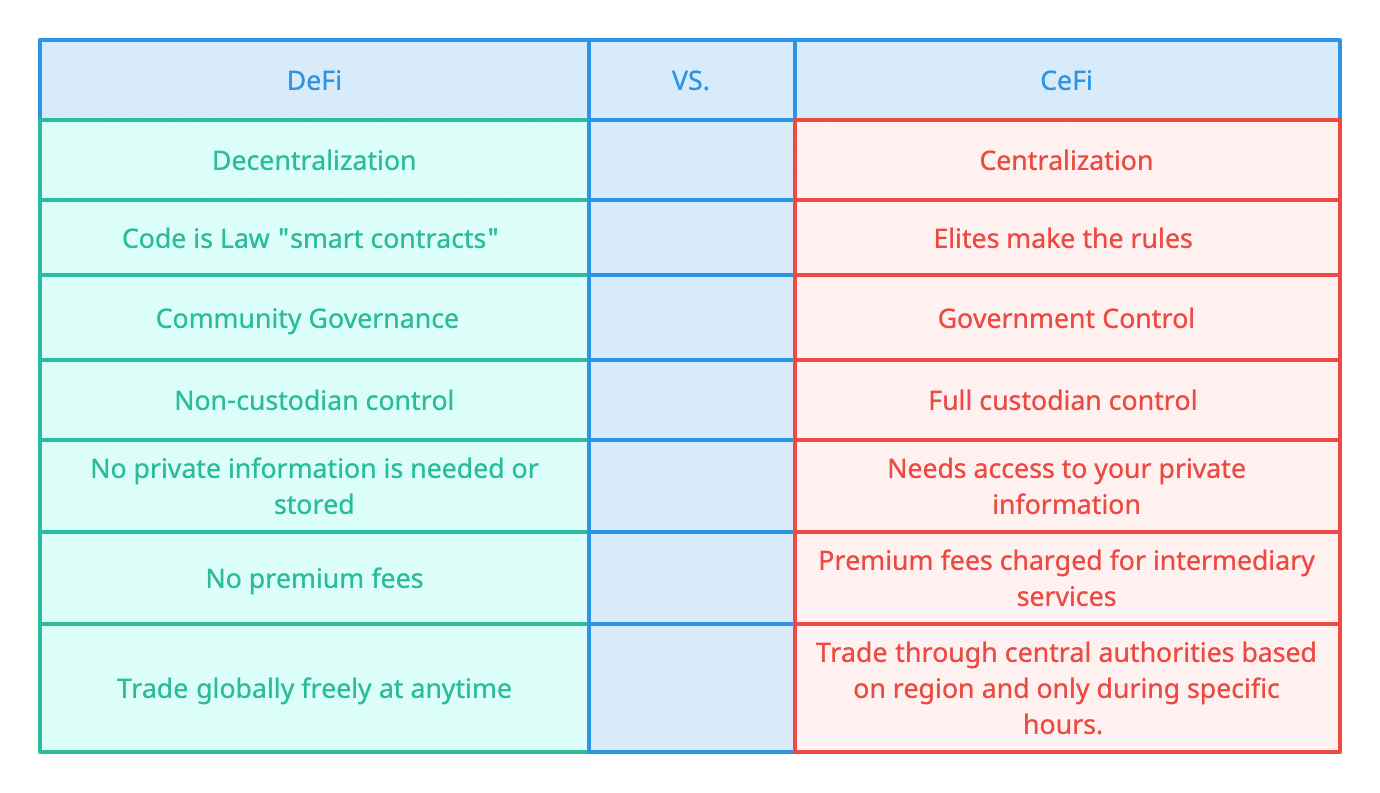
Why use Defi?
With DeFi, there is the opportunity to give everyone access to financial freedom in a truly equitable manner. It is a space where free trade is possible, but not without risk of course. Unlike traditional finance, DeFi much, like the rest of the crypto universe, is not regulated and lacks investor protection. The high volatility of the whole cryptocurrency market is another issue investors and users of platforms must be aware of, this can often lead to mass liquidations, locking of funds on exchanges, network congestion, and more.
All of these factors make DeFi a higher risk, but what in life is not a risk? What type of opportunities have you ever experienced without some kind of trust placed into a risk. The point of DeFi is not to reduce risk necessarily, the main purpose is to promote a truly decentralized "free" economic system. The likes of which you only learn about in textbooks. A financial system where people can partake without needing to hand over their personal information, without bias, and without a centralized authority controlling it.
Here is a list of some of the current and future applications for DeFi:
- Asset management
- Lending
- Borrowing
- Derivatives Trading
- Options Trading
- Global Payment Solutions
- Crowd Funding
- Insurance
How does DeFi work?
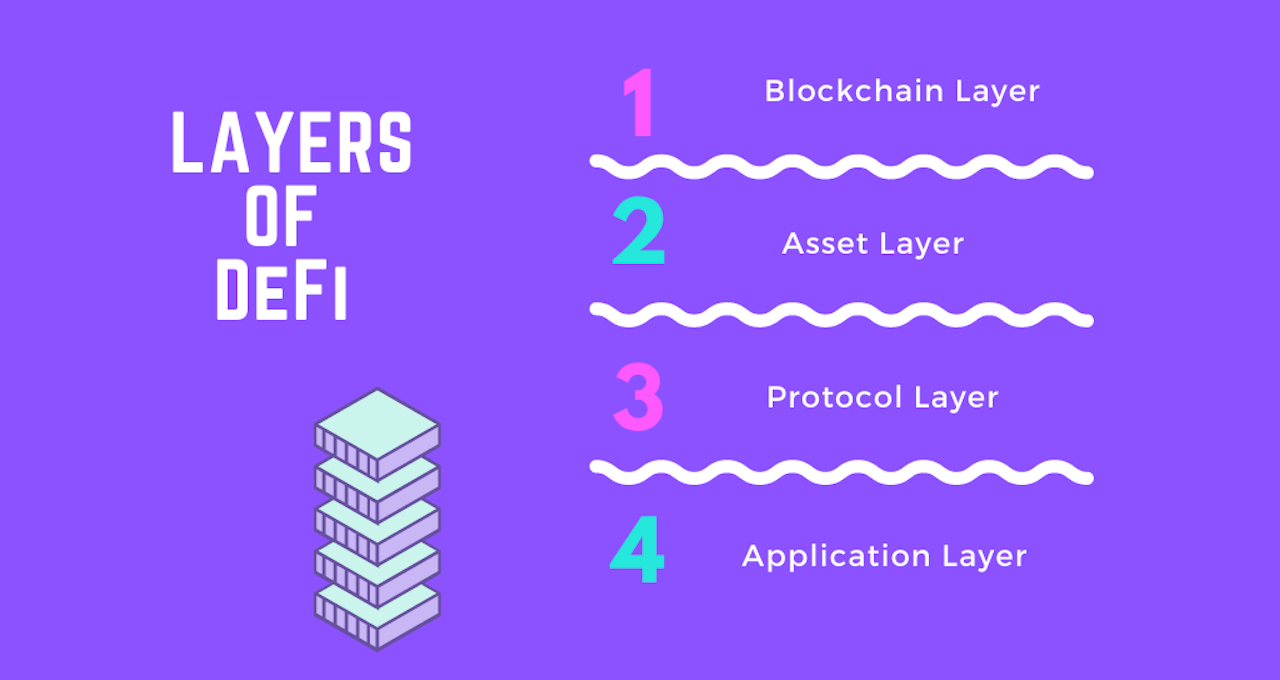
We can think about how DeFi works as these four layers:
- The blockchain Layer
- The host blockchain that the DeFi project is built on. It maintains the transaction history and state of accounts or UTXOs.
- The asset layer
- Where the native assets like ADA, ETH, and the other tokens live.
- The protocol layer
- The collection of smart contracts which operate the protocol and provide the various DeFi services.
- The Application Layer
- The various decentralized applications or products used by the community to manage, interact and govern the protocol.
The Blockchain Layer
The host blockchain plays a key role in DeFi applications and services. They affect the speed of txs, security, interoperability between protocols, smart contract functionality, and more. DeFi protocols are just a collection of smart contracts that run various services.
It is why the DeFi ecosystem today is primarily built on Ethereum using ERC-20 tokens and Ethereum Smart contracts. However, this won't be the case anymore since Cardano has launched native asset support and smart contract functionality on its blockchain this year. Cardano is not the only smart contract capable blockchain out there trying to get into the DeFi space. Two notable mentions are Solana and Avalanche.
The Asset Layer
Each blockchain has a native cryptocurrency or digital asset that is vital in using various DeFi protocols. The tokens are used as collateral in DeFi protocols, traded for other tokens like governance tokens, or to earn interest or governance tokens.
The Protocol Layer
The smart contracts that run DeFi protocols replace the need for a centralized authority or intermediaries when settling transactions. A smart contract is similar to a financial institution in the way it works. You deposit your assets as collateral into a DeFi protocol, which has a set of smart contracts that are the services. These can be lending, borrowing, transferring, swapping tokens, and payments. Unlike with traditional finance, you never actually give up custodianship of your digital assets using smart contracts.
Another benefit is that smart contracts are immutable once they are live on the blockchain. Adding security and trust in the fact a contract will execute as planned by the parties involved.
The DeFi smart contracts are open-source and publicly available to allow for analysis, audits, and improvements. As I declared earlier, smart contracts are immutable that suggests bad contracts are identified and flushed out quickly by users. As smart contracts become even easier to understand for non-experienced programmers, the trust level in DeFi will continue to grow.
The Application Layer
The way users interact with various DeFi protocols varies, but typically they have what are known as Dapps or decentralized applications. These applications provide a user interface and the ability to interact with the underlying protocol's functionality. A few examples of Dapps are wallets like Metamask, governance or voting applications, digital identity apps, , , and . For more information about Dapps, please in which we discuss them in greater detail.
Here is a video that walks through how exactly DeFi layers interact
Here is a small list of some of the top projects that are currently in the DeFi space:
| Project | DeFi Service | |
|---|---|---|
| AAve | Lending | |
| Lending | ||
| Curve Finance | DEX | |
| Uniswap | DEX | |
| yearn.finance | Assets | |
| Synthetix | Derivatives | |
| Flexa | Payments |
If you would like to see all the projects in the DeFi ecosystem please visit DeFi Prime.
Last updated on 4 years ago
Edit on GitHubGet notified when we release new content
Sign up for our newsletter to stay up-to-date with the latest Armada Alliance news and updates.